3D Printing vs Traditional Manufacturing: Which is Right for Your Project?
Introduction to 3D Printing and Traditional Manufacturing
In recent years, 3D printing has emerged as a groundbreaking technology that offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. However, deciding between 3D printing and traditional manufacturing for your project can be challenging. Both have their unique strengths and limitations, and understanding these differences is crucial to making an informed choice.
Traditional manufacturing, which includes methods like injection molding, CNC machining, and casting, has been around for decades, offering reliability and precision. In contrast, 3D printing is a relatively new technology that has gained popularity due to its flexibility and ability to produce complex geometries.
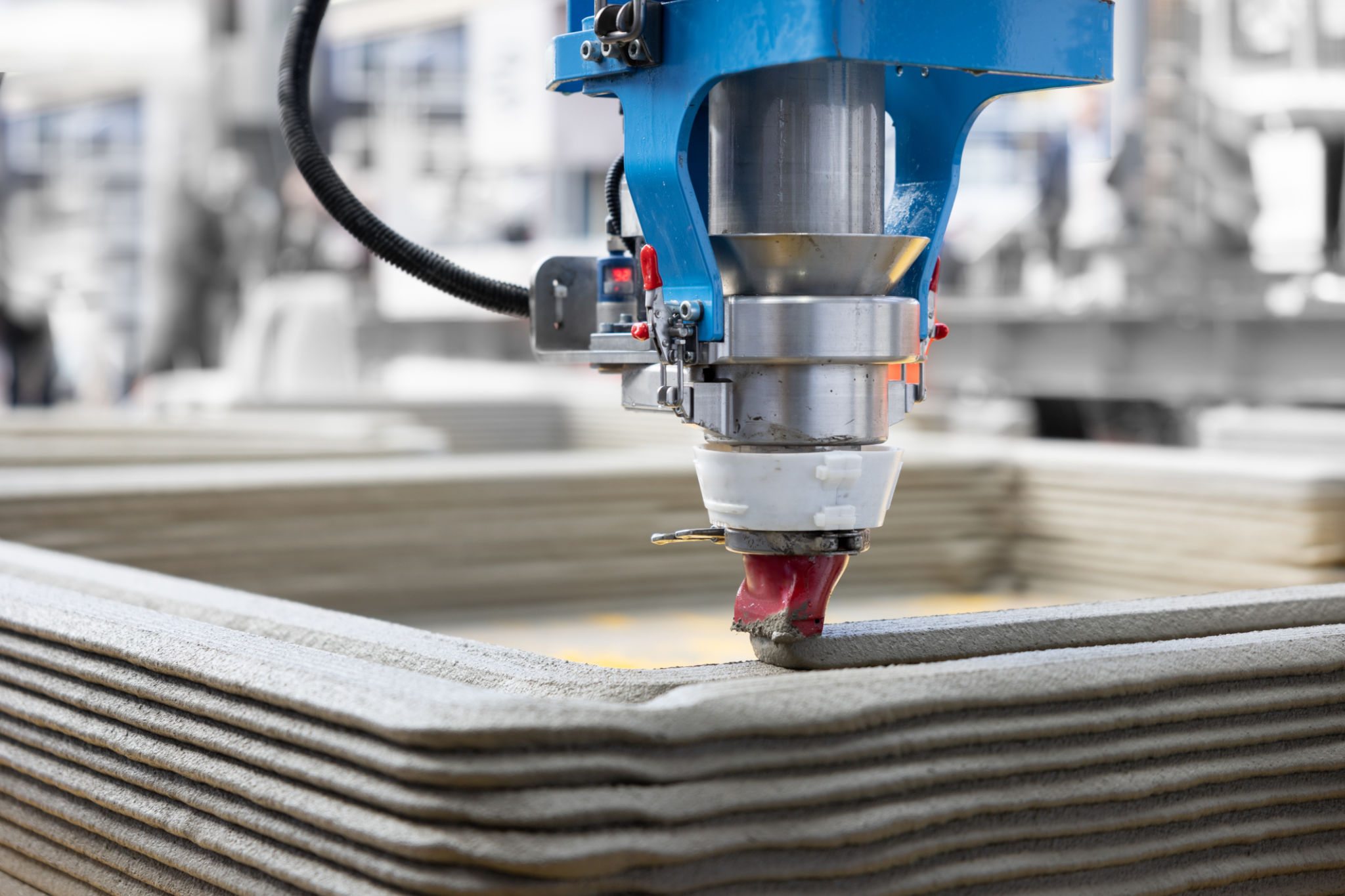

Understanding Cost Implications
One of the most significant factors in deciding between 3D printing and traditional manufacturing is cost. Generally, 3D printing involves lower initial costs because it requires less setup and tooling. This makes it an attractive option for prototypes and small production runs. However, as the volume increases, the cost per unit for traditional manufacturing tends to decrease, making it more economical for mass production.
It's essential to consider not only the production costs but also the material costs. 3D printing materials can be more expensive than those used in traditional manufacturing. Therefore, a detailed cost analysis based on your project's scale and material requirements is necessary.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
When it comes to design possibilities, 3D printing offers unparalleled flexibility. It allows for the creation of intricate designs that would be impossible or very costly with traditional methods. This capability makes it ideal for projects that require customized or complex parts.
Traditional manufacturing, on the other hand, may require redesigning a part to fit within manufacturing constraints, leading to potential design compromises. However, for simpler designs or those that need high precision, traditional methods can be more suitable.
Production Speed and Efficiency
The speed of production can also influence your choice between 3D printing and traditional manufacturing. For rapid prototyping and small batches, 3D printing is often faster because it eliminates the need for creating molds or setting up machinery.
Traditional manufacturing may take longer initially due to setup times, but once the process is established, it can produce large quantities quickly and efficiently. Therefore, if time-to-market is a critical factor for large-scale production, traditional manufacturing might be more advantageous.
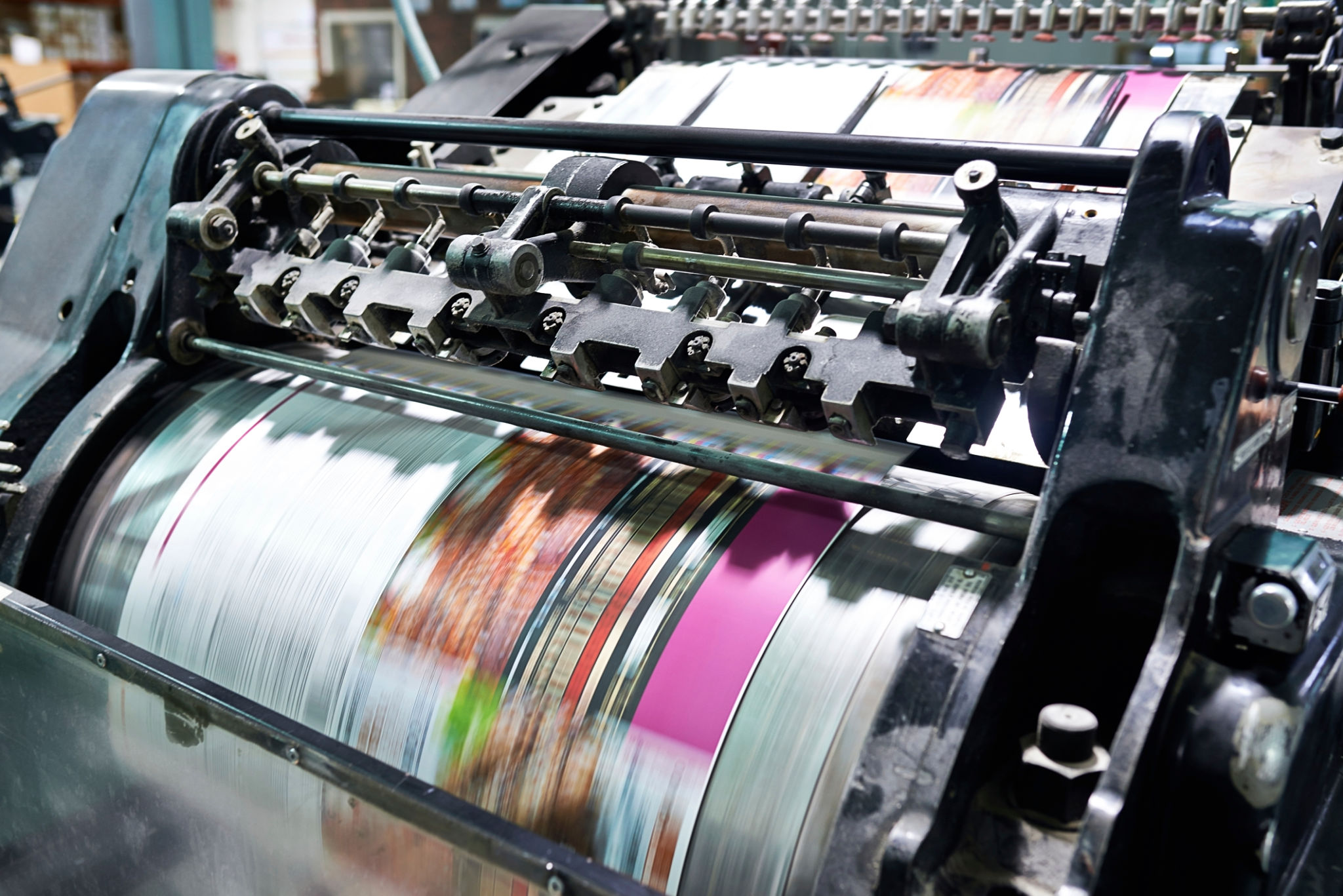

Material Selection and Properties
Another consideration is the range of materials available for each method. Traditional manufacturing offers a wider variety of materials with established properties, making it suitable for projects requiring specific material characteristics like strength or temperature resistance.
While 3D printing materials are expanding rapidly, they still might not match the diversity or durability of traditional materials. However, advancements in 3D printing technology continue to improve material options and their properties.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Ultimately, the decision between 3D printing and traditional manufacturing depends on your project's specific requirements. Consider factors such as cost, design complexity, production speed, and material needs when making your choice.
Both methods have their place in modern manufacturing, and sometimes a hybrid approach—using both technologies—can offer the best of both worlds. By carefully evaluating your project's needs, you can select the most suitable manufacturing method to ensure success.