Case Study: Transforming Ideas into Reality with 3D Printing
Introduction to 3D Printing
The advent of 3D printing has revolutionized the way we approach design and manufacturing. This cutting-edge technology allows for the rapid transformation of concepts into tangible products, empowering creators and businesses alike to innovate like never before. From custom prototypes to intricate designs, 3D printing is paving the way for a new era of production.
The ability to create complex structures with precision and ease is one of the hallmarks of 3D printing. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which often require molds and extensive setup, 3D printing streamlines the production process. This means faster turnaround times and increased flexibility in design alterations.
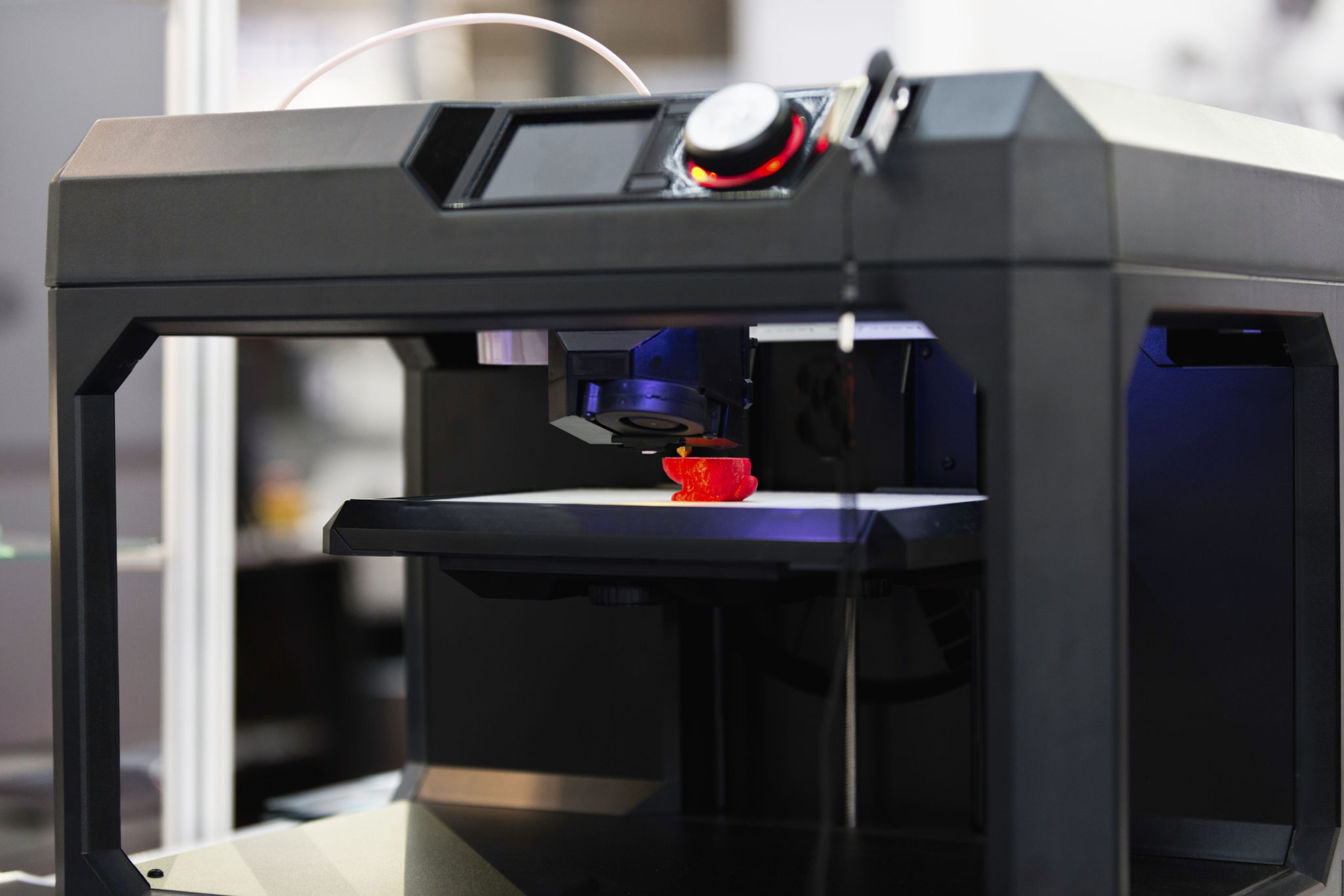
The Process of Bringing Ideas to Life
At the heart of 3D printing is the conversion of digital models into physical objects. The process begins with a digital design, usually created using CAD software. This design is then sliced into layers, which the 3D printer uses as a blueprint to construct the object layer by layer.
This layer-by-layer approach allows for remarkable detail and precision, making it possible to produce items that would be difficult or impossible to create using conventional methods. The adaptability of this process means that even complex geometries and intricate details can be realized with minimal effort.

Materials and Techniques
3D printing is not limited to a single type of material. In fact, a wide range of materials can be used, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biological substances. Each material offers unique properties and advantages, enabling users to select the best option for their specific needs.
Various techniques such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) offer different benefits depending on the application. For instance, FDM is known for its accessibility and affordability, while SLA provides higher resolution prints.

Real-World Applications
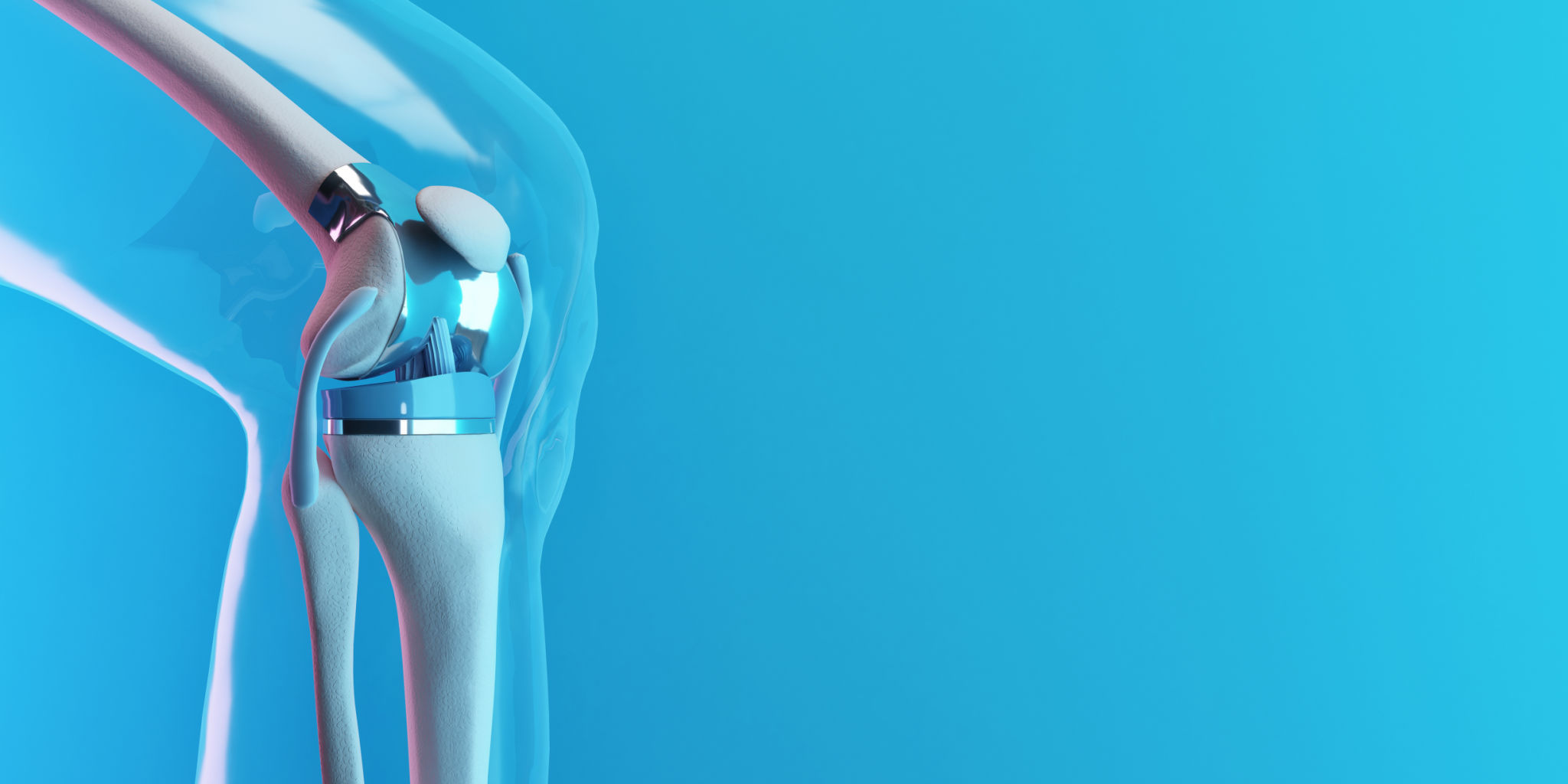
The versatility of 3D printing has led to its adoption across numerous industries. In healthcare, for example, it is used to create custom prosthetics and implants tailored to individual patients. This not only enhances comfort but also improves functionality significantly.
In the automotive and aerospace sectors, 3D printing facilitates the production of lightweight components that enhance performance while reducing fuel consumption. Additionally, it allows for rapid prototyping, accelerating the development of new models and technologies.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its many advantages, 3D printing is not without challenges. Issues such as material limitations, production speed, and post-processing requirements can pose hurdles. However, ongoing research and development efforts are continuously addressing these challenges.
Looking ahead, the future of 3D printing is bright and full of potential. As technology advances, we can expect even greater precision, faster production times, and a broader array of materials. These innovations will further cement 3D printing's role as a transformative force in the world of design and manufacturing.
